Iris
This page contains the abbreviated code for the iris modeling example. For a detailed walkthrough, look at the RSample through Workflows tutorials. Note that this example uses a workflow object to create the final predictions, and thus the recipe and parsnip model are not prepped or fit independently.
library(tidymodels)
# defining data_iris
data_iris <- bind_cols(all_of(iris),
row = 1:nrow(iris))# RSample - generate data splits
data_split <- initial_split(data_iris, prop = 3/4)
testing <- testing(data_split)
training <- training(data_split)# Recipes - define and apply preprocessing steps
iris_recipe <- recipe(Species ~ .,
data = training) |>
update_role(row, new_role = "ID") |>
step_corr(all_numeric_predictors()) |>
step_normalize(all_numeric_predictors()) |>
step_rename(Row = row) # Parsnip - create a model
rf <- rand_forest() |>
set_mode("classification") |>
set_args(trees = 200) |>
set_engine("randomForest")# Workflows - bundle recipe and model together and generate predictions
iris_wkf <- workflow() |>
add_recipe(iris_recipe) |>
add_model(rf) |>
fit(training)
iris_preds <- iris_wkf |>
augment(testing)# Yardstick - evaluate performance
my_metrics <- metric_set(sens, spec, accuracy)
iris_preds |>
my_metrics(truth = Species, estimate = .pred_class)## # A tibble: 3 × 3
## .metric .estimator .estimate
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 sens macro 1
## 2 spec macro 1
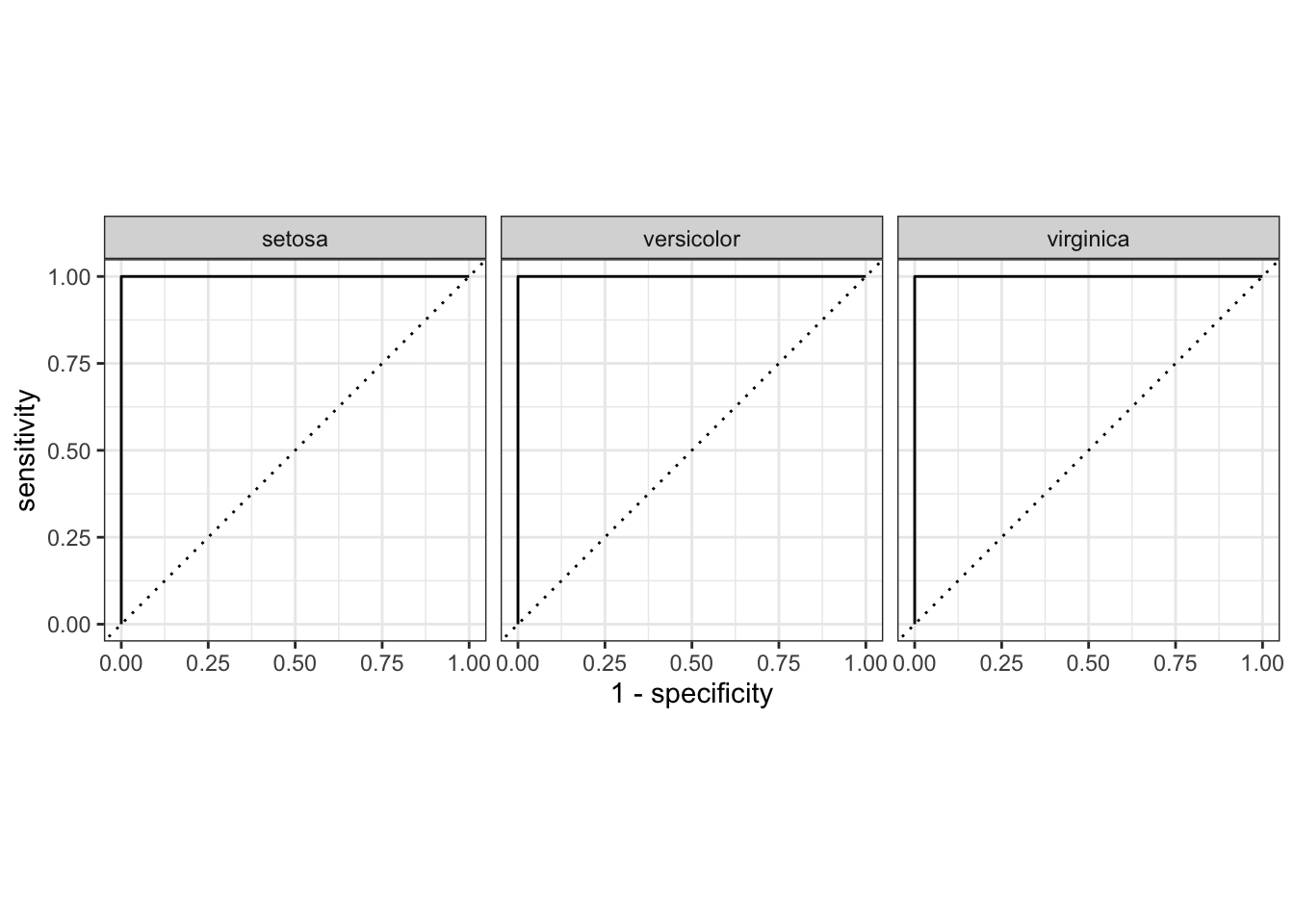
## 3 accuracy multiclass 1iris_preds |>
roc_curve(Species, .pred_setosa:.pred_virginica) |>
autoplot()